Discrete Points In One-Demension
About 1369 wordsAbout 5 min
2024-1-25
 本文介绍了一维离散点问题的处理方法
本文介绍了一维离散点问题的处理方法
问题背景
当我们需要处理的数据范围零散的分布在一个很大的范围内,我们无法采用顺讯存储将点的真实位置作为一个顺讯表的下标来对问题进行建模。
一个例子
分析
显然,无法像正常前缀和那样使用一个一维数组来处理,我们无法开出这么长的数组(对于 −109≤ x ≤109, 需要 2 _ 109 _ 4 Byte 也就是 大约 7.5GB 内存)。
做法 1
流程
- 构造一个
pair<int , int> point; 每个一point记录在数组的x位置加上一个c。 - 在数组中插入首尾哨兵
{(+/-)INF , 0},保证在之后查找中都能返回一个语义正确的位置。 - 将所有
point存储在points数组中。并按point的操作位置x对数据排序。 - 对于
points数组求前缀和。 - 对于每一组查询
l和r,使用二分查找找出他们在points中对应的真实下标。- 对于
l,找第一个大于等于 l 的被记录下标。 - 对于
r,找第一个小于等于 r 的被记录下标。
- 对于
- 利用这个真实下标求出前缀和。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<utility>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+10, INF = 1e9 + 10;
typedef long long ll;
ll presum[N];
typedef pair<int , int> pos;
vector<pos> points;
int n , m;
int find_ge(int n)
{
int l = 0 , r = points.size()-1;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(points[mid].first >= n) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
int find_le(int n)
{
int l = 0 , r = points.size() - 1;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = (l + r + 1) >> 1;
if(points[mid].first <= n) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
return r;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
int x , c;
//
points.push_back({-INF , 0});
points.push_back({INF , 0});
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d" , &x , &c);
points.push_back({x , c});
}
sort(points.begin() , points.end() , [](pos &a , pos &b){return a.first < b.first;});
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
{
presum[i] = presum[i-1] + points[i].second;
}
int l , r;
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d %d" , &l , &r);
// 使用二分查找第一个大于等于l的坐标和第一个小于等于r的坐标
l = find_ge(l); r = find_le(r);
printf("%d
" , presum[r] - presum[l-1]);
}
}复杂度分析
这个做法采用了较少的额外空间,但代码量较大。二分查找的处理考验对于二分查找的理解。
- 时间复杂度
O(max(nlg(n) , mlg(n))), 左边是排序points的时间,右边是进行二分查找的时间。 也可以记为O(max(n , m)lg(n)) - 空间复杂度 算法的空间复杂度为
O(n)
要点
二分答案不存在
设想这样的场景, 在序列[1 , 2 , 3 , 4, 5] 中使用查找第一个大于等于 6 的数。这样答案不存在,二分会给出错误的答案。端点哨兵的加入保证任何二分答案都是正确的。
端点的选取
首先要有一个认识,points数组中可能存在对某一个位置的重复操作。所以pionts和presum数组有如下的关系。
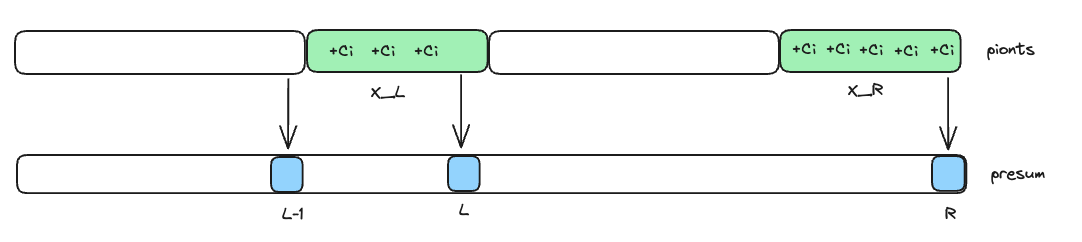
在求 presum[r] - presum[l-1]时,对于右端点X_R,其points数组中最右位置对应的presum记录记录X_R的正确信息。对于L-1同理,比X_L的最左减一的位置记录了X_L的正确信息。 所以在二分查找,需要找到
- 第一个小于目标区间右侧区间的记录
- 第一个大于目标区间左侧区间的记录
做法 2
流程
- 将操作和查询都插入
std::map<int , int> record中,同时查询插入查询数组queries, map会自动进行升主键排序,同时支持遍历。遍历并求前缀和 presum 数组,同时将坐标映射关系插入unordered_map<int , int> dict中。- 遍历
queries数组, 从坐标映射关系得到真实的端点,利用 presum 数组给出答案。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<utility>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
map<int , int> records; unordered_map<int , int> dict;
typedef pair<int , int> query;
vector<query> queries;
const int N = 3e5+10 , INF = 1e9;
int presum[N];
int main()
{
int n , m; cin >> n >> m;
int x , c , l , r;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d" , &x , &c);
records[x] += c;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d" , &l , &r);
records[l] += 0; records[r] += 0;
queries.push_back({l , r});
}
int index = 1;
for(const auto& record : records)
{
presum[index] = presum[index-1] + record.second;
dict[record.first] = index++;
}
for(const auto& query : queries)
{
int l = query.first , r = query.second;
l = dict[l] , r = dict[r];
printf("%d
" , presum[r] - presum[l-1]);
}
}复杂度分析
该算法相对好写。
- 时间复杂度 插入
map的复杂度为O((n+2m)lg(n + 2m))遍历的复杂度为O(n+2m) - 空间复杂度 维护 map 的复杂度为
O(n+2m) 维护 presum 的复杂度为O(n+2m)
要点
std::map map 表现为键值对,其底层结构是一棵红黑树。红黑树是一种自平衡二叉树,它帮我们解决了两个问题。
- 对于操作位置的排序
- 合并同一位置的相同操作
records[x] += c;- 如果这个记录不存在,那么这条语句会构造该记录,并将其值符零。
std::unordered_mapunordered_map表现为键值对,其底层结构是哈希表。对于哈希表,其插入和查询性能都是O(1), 但不支持遍历。它帮我们存储了操作位置和存储位置的映射关系。
Copyright
Copyright Ownership:Pray0
License under:Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY-4.0)