A-Star

A-Star加入了启发式函数,使得路径搜索更为高效。本文讲解了A-Star算法的一些细节。
概述
A-Star的诉求是通过一定的启发式条件剪枝掉一定的搜索空间。考虑在二维网格中搜索两个点的最短路径。如果使用宽搜类算法,其搜索路径如图所示。

可以想见的是,如果在搜索过程加上终点位置这一信息之后,每个搜索点的位置就不再平等,距离终点的终点距离更近的点成为了更好的点,如果可以优先搜索这些点,那么可以更快的搜索到终点。
基于这样的思想A-Star算法便诞生了。观察其搜索路径图示。

估计函数
考虑这样细节:
- 因为障碍的存在,我们不能准确估计哪些点是搜索终点更近的
- 视觉上更近的点在搜索路劲中可能更远
正如这一节的标题,对于距离搜索终点的距离是一种估计。
估价的细节
估价函数有这样一些要求
- 搜索目标点必须是存在,换言之,这个搜索过程必须是有解的。
- 估价函数的取值范围需要满足该不等式
- 真实值 >= 估计值 >= 0
- 估价函数需要反应真实的单调性常见的估价函数设计思路
- 基于距离 比如曼哈顿距离 欧式距离 对角距离
- 基于真实的最短距离
算法过程
- 同时计算当前的搜索距离(成本)
D和距离终点的估价距离F。这二者的和反应了路径的估计总成本。 - 维护一个优先队列,每次弹出路径估计总成本最低的节点出队,更新其他节点的距离。
- 当搜索终点第一次出队时,结束搜索,这时的路径为最短路径。
相关证明
正确性
证 : 第一次搜索到终点为最优路径。
- 假设第一次搜索到终点
e不为最优,那么现在搜索路径中存在某个待选点w, 经过w的路径是最优的真实路径。- 则
D(e) + F(e) >= real(d) >= D(w) + F(w)
- 则
- 那么便推出了矛盾,
w应该先于e出队
图解
考虑这样的情况
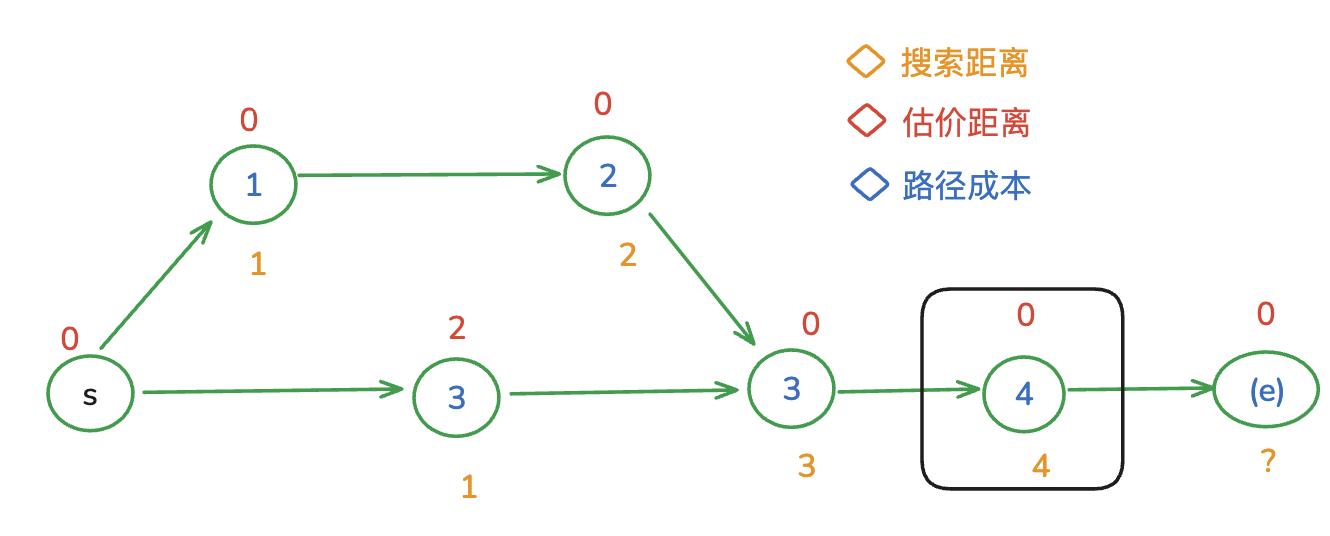 路径会在框示节点回溯,从起点的右侧节点开始重新更新底侧路径的搜索距离。
路径会在框示节点回溯,从起点的右侧节点开始重新更新底侧路径的搜索距离。
对于其他节点,第一次搜索到并不一定是最小的。 终点搜索正确性是由估价函数的取值范围来保证的。
例题
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<utility>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int , string> PII;
// 由于每次只移动一个节点 所以可以使用曼哈顿距离来进行估价
int cal(string state)
{
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < state.size(); i ++ )
if (state[i] != 'x')
{
int t = state[i] - '1';
res += abs(i / 3 - t / 3) + abs(i % 3 - t % 3);
}
return res;
}
string Astar(string start)
{
priority_queue<PII , vector<PII> , greater<PII>> q;
// 维护每个点的前置节点和对应的移动方式
unordered_map<string , pair<string , char>> prev;
unordered_map<string , int> dist;
string end = "12345678x";
q.push({cal(start) + 0 , start}); dist[start] = 0;
int tx[] = { 0 , 0 , 1 , -1 };
int ty[] = { 1 , -1 , 0 , 0 };
string ops = "rldu";
while(q.size())
{
PII f = q.top(); q.pop();
string state = f.second; int step = f.first;
if(state == end) break;
int idx = state.find('x');
int x = idx / 3 , y = idx % 3;
string source = state;
for(int i = 0 ; i <= 3 ; i++)
{
int nx = x + tx[i] , ny = y + ty[i] , nidx = nx * 3 + ny;
if(nx >= 0 && nx <= 2 && ny >= 0 && ny <= 2)
{
swap(state[idx] , state[nidx]);
if(dist.count(state) == 0 || dist[state] > step + 1)
{
dist[state] = step + 1;
prev[state] = { source , ops[i] };
q.push({dist[state] + cal(state) , state});
}
swap(state[idx] , state[nidx]);
}
}
}
string res = "";
while(end != start)
{
res += prev[end].second;
end = prev[end].first;
}
reverse(res.begin() , res.end());
return res;
}
int main()
{
string start , seq;
char c;
while(cin >> c)
{
start += c;
if(c != 'x') seq += c;
}
// 求解逆序对
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i++)
for(int j = i ; j < 8 ; j++)
if(seq[j] > seq[i]) cnt++;
// 逆序对是偶次变换的 如果初始逆序对为奇数 则无解
if(cnt % 2 == 1) {
cout << "unsolvable";
return 0;
}
cout << Astar(start);
}#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e3 + 10 , M = 2e4 + 10;
int h[N] , rh[N] , e[M] , w[M] , ne[M] , idx;
int dist[N] , inQ[N];
int cnt[N];
typedef pair<int , pair<int , int>> PIII;
void add(int h[] , int a , int b , int c)
{
w[idx] = c; e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a] ; h[a] = idx++;
}
void init()
{
memset(h , -1 , sizeof h);
memset(rh , -1 , sizeof rh);
memset(dist , 0x3f , sizeof dist);
}
// 在方向图中求出终点到其他点的最短距离
void spfa(int start)
{
queue<int> q; q.push(start);
dist[start] = 0; inQ[start] = true;
while(q.size())
{
int f = q.front(); q.pop(); inQ[f] = false;
for(int i = rh[f] ; i != -1 ; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(dist[j] > dist[f] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[f] + w[i];
if(!inQ[j])
{
q.push(j) ; inQ[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
int Astar(int s , int end , int k)
{
priority_queue<PIII , vector<PIII> , greater<PIII>> heap;
heap.push({0 + dist[s] , {0 , s}});
while(heap.size())
{
auto t = heap.top(); heap.pop();
int vertex = t.second.second , distance = t.second.first;
cnt[vertex] ++;
// 第一次访问终点 k 次是即为答案
if(cnt[end] == k) return distance;
// 入队所有可能的点
for(int i = h[vertex] ; i != -1 ; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
// 如果一个点已经被访问了超过 k 次 那么它不可能在 通往终点的 k 短路上
if(cnt[j] <= k)
heap.push({distance + dist[j] + w[i] , {distance + w[i] , j}});
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
init();
int n , m; cin >> n >> m;
while(m --)
{
int a , b , c; cin >> a >> b >> c;
add(h , a , b , c); add(rh , b , a , c);
}
int s , t , k; cin >> s >> t >> k;
spfa(t);
if(s == t) k ++; // 如果起点等于终点 因为是至少需要经过一条边 所以多一条路径
cout << Astar(s , t , k);
}Copyright
Copyright Ownership:Pray0
License under:Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY-4.0)